The word subcontinent implies the sub-division of a continent with its proper geographical, political, and cultural identity. Also, the land has to be made of a large mass. And The Indian subcontinent has it all. This subcontinent comprises countries like India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Maldives, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
Now, as we know, the Indian subcontinent is one of the unique creations of Earth, and so many elements and features made those countries into a subcontinent. Therefore, people need to know about these basic geographical elements of the world.
Quick Access
Geographical Features
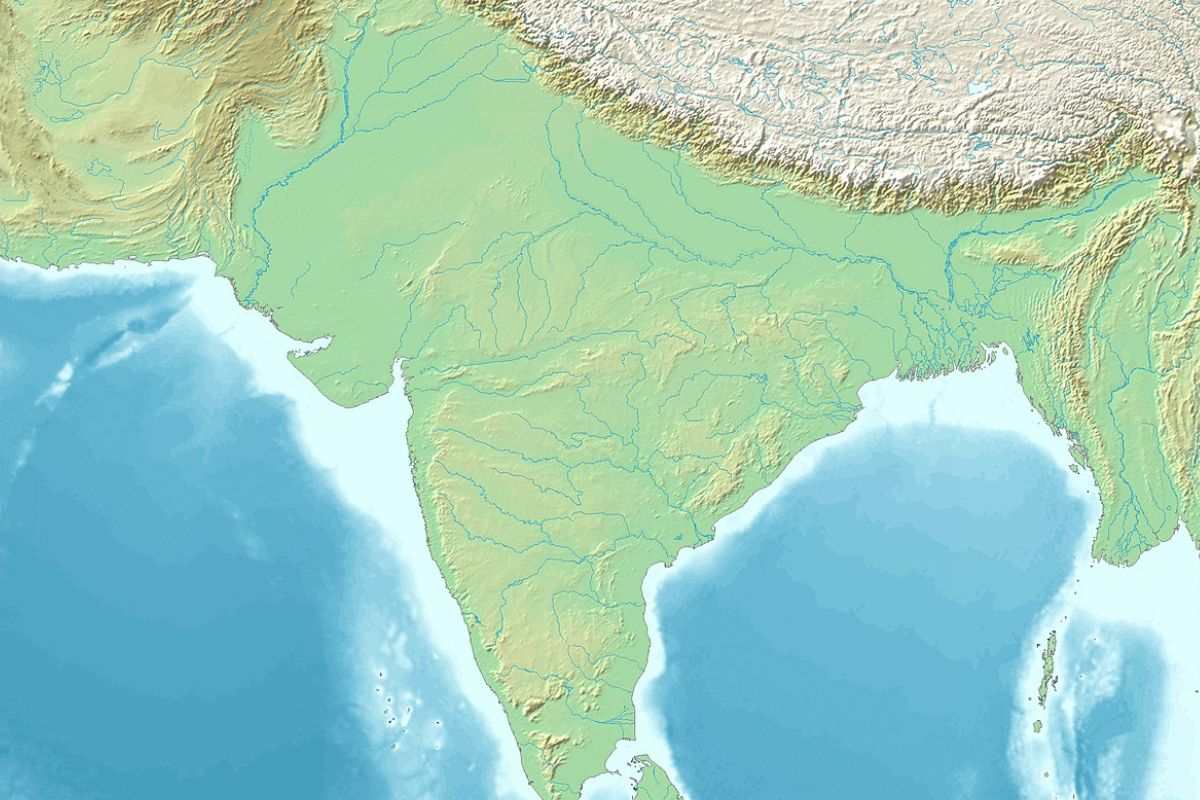
From its northern boundary, the peninsular portion in South-Central Asia is blocked by the Himalayas, Karakoram, and the Hindu Kush mountains. In the west, it is bounded by parts of the Hindu Kush, Spīn Ghar, Sulaiman Mountains, Kirthar Mountains, and Pab range, among others, along with the Western Fold Belt in the border. In the east, the place is blocked by Naga, Patkai, Lushai, and Chin hills. On the south, southeast, and Southwest locations of the place as a boundary lies the Bay of Bengal, the great Indian Ocean, and the Arabian Sea.
For all this geographical diversity, so many landforms are available in India. Those landforms are the Himalayan mountains, the northern plains, the Indian desert peninsular plateau coastal plains, and the Islands.
India is a country or a subcontinent situated in the southern area of Asia. India, a subcontinent, is made up of a huge landmass. It has all the elements that a subcontinent requires, such as the Himalayas region in the Northwest, the Gangetic plains in the southeast, and the plateau territory in the north.
Historical Perspective
According to the historical overview, the continent signifies a subdivision with its own geographical, political, and cultural identity. Also, it’s a place that requires a large land mass, which is smaller than a continent. Now, historians and geographers find all these elements in the South Asian region, mainly in India.
When the geographers and the explorers came to know about this place, to identify or while studying the subcontinent, they addressed the whole region with the name India before the partition when the whole of the Indian subcontinent was under the control of the British Raj. It was easier for historians to refer to the subcontinent by the name India. Another reason the subcontinent was called India is because of the regions surrounding and southeast of the Indus River.
By the British Empire and its successors, the Indian subcontinent used to be known as India for many years. Then, with time, the place became known as South Asia in Europe and North America. But then, due to issues with the region’s contemporary political boundaries, the name of the subcontinent was changed to the Indian subcontinent.
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics has a huge role in India’s geology because the Indian plate collided with The Eurasian plate. The zone where these two plates collide is prone to major earthquakes as it is geologically active.
The Indian plate used to be a part of the supercontinent, Gondwana. But the plate broke away from Gondwana, carried the insular India with it, and collided with The Eurasian plate almost 55 million years ago.
As a result of this collision, the Himalayas range is made. Hence, plate tectonics can be considered as a primary reason for India being a proper subcontinent.
Cultural and Linguistic Diversity
India’s cultural richness and diversity
India is considered one of the countries enriched with cultural diversity. The main reason for its cultural diversity is its location and religion. Throughout India, many significant fusions of cultures are available between Muslim, Buddhist, Sikh, and many other tribal populations.
India is a Hindu-majority country and has a large Muslim population. But what matters more is that India is the birthplace of Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Jainism, and other religions. Even though all these religions are spread all over India, these religions have a lot of cultures within them and even have a great linguistic influence.
How cultural and linguistic differences are related to the subcontinent status
After the Indus civilization, as the influence of Indo-Aryan culture in India, more than 78.05% of Indians spoke the Indo-Aryan language. Then, 19.64% of Indians speak Dravidian languages. The other 2.31% is used for minor language families and isolates. However, the major language from which most of the languages in India are created is Sanskrit.
Examples of different cultures and languages within India
Now, based on the culture, these languages have many other sublanguages. And because of it, India has more than 300 spoken languages. The most spoken language in India is Hindi, as it is the national language of India. However, English is also known to many Indians as it allows them to be a part of the international culture.
Based on different cultures, many native languages within India are Indian communication. For example, in Central and West India, people speak Gujarati, Marathi, etc. In northern India, the Indians speak Punjabi, Kashmiri, etc.; in East India, people speak Bengali, Odiya, Bihari, etc. The Dravidian languages are mostly spoken in South India: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam. In India, most of the states have language for the location.
Historical and Cultural Significance
India’s historical significance in the context of the subcontinent
The subcontinent India has a rich history, as it started with the Indus Valley civilization during the pre-Vedic era and the arrival of Aryans during the Vedic period. However, the political unit of the subcontinent began under the rule of Chandragupta Maurya. The Maurya Empire, from 321 to 185 BCE, ruled the whole North West of the Indian subcontinent. Then, During the rise of the Guptas with time, the Empire attained the entire Northern part of the subcontinent. During the rule of the Guptas, India experienced enormous cultural and intellectual achievements; for the Hindu religion, it was the golden era. And after that, the Mughals, the Turkic lineage from Central Asia, arrived in Delhi. They were not the first Muslim ruler in the subcontinent but the most prominent Empire to conquer most of the Indian subcontinent. Finally, when the Mughal Empire started to suffer and lose power, the British Raj began to take control.
The Indus Valley Civilization and other ancient Cultures
The first civilization of India was the Indus Valley civilization. This civilization was situated in Pakistan, northeast Afghanistan, and Northwest India. Because of the Indus Valley, the civilization flourished and became one of the three most prominent civilizations. It was when the concept of economy and cities were introduced to people. Some people are used to making art, technology, and the concept of writing. Then, even though the civilization has spread to different locations in Asia, the Indus Valley civilization and the Indo-Aryan migration is the only reason India is a Hindu-majority country.
How India’s cultural contributions have shaped its identity
Throughout history, India has experienced many cultural changes and flourished culturally in many different ways. The history of the subcontinent started with the Indus civilization. It was ruled by Hindu empires like the Maurya and Gupta, then the Muslim Rulers Mughals, and ultimately the British Raj. Not only that, it’s a place where Tirthankaras, Parshvanatha, and Mahavira propagated Jain philosophy. Buddhist philosophy was founded, and Sikh philosophy was crystallized in Guru Granth Sahib. Therefore, history plays a huge role in building the Indian culture and becoming the subcontinent it is now.
Comparison with Other Subcontinents
India and other subcontinents around the world
There are six subcontinents worldwide: the Arabian Subcontinent, Southern America, Southern Africa, Alaska, Greenland, and the Indian Subcontinent. Among the other subcontinent, the Indian subcontinent is widely recognized and has all the features that a subcontinent requires.
Similarities and differences
The Arabian Subcontinent has political boundaries and geographical features similar to the Indian subcontinent. But there are things the Arabian subcontinent doesn’t have. Like the Indian subcontinent, there is no river, forest, or futile plain land in the Arabian peninsula. It mainly has coastal plains, but the coastline is way smaller than India. Also, India is full of cultural diversity, where Arabs aren’t.
The southern cone of South Africa is mostly similar to the Indian subcontinent in geographical features; politically, it’s mostly Argentina and Chile that are part of the subcontinent. In land mass and cultural aspects, the Indian subcontinent is much more significant.
Similar to the subcontinent in India, Southern Africa has geographical, political, and cultural. But geographically, the subcontinent is smaller than the Indian subcontinent, and the place has lesser political diversity. However, the place is known as the rainbow nation for its cultural diversity, but no other place has as many languages and religions as India.
Alaska is a subcontinent with no cultural significance like India. It is only considered a subcontinent because of its distinctive geography and size.
Most people don’t consider Greenland as a subcontinent. Still, the only reason Greenland sometimes gets referred to as a subcontinent is that it shares the North American plate, a tectonic plate.
What sets India apart as a subcontinent
So, we can say that India is a country filled with various cultures, has very active political diversity, and is rich in geographical features. No matter how many subcontinents there are, no place has this much diversity and has huge landmarks like the Indian subcontinent.
Conclusion
People already know about the continents and the huge land masses with all the required geographical diversity, like mountain plateaus, plains, deserts, and islands. But for many, it’s not clear why India is considered a subcontinent. However, it’s a confusion that can be solved easily.
It is proven that India has geographical, cultural, and political features that other places have. And even though the Indian subcontinent is made with other countries, the major part of it is India.
Therefore, the readers can understand that India, a subcontinent, is unique in its way, which even many renowned geologists and historians agree on.
Additional Resources-
supposing anyone wants to know more about the Indian subcontinent. They should research it online or read books like The Incredible History of India’s Geography by Sanjeev Sanyal.